Real-time near-infrared (NIR) face alignment holds significant importance across various domains, such as security, healthcare, and augmented reality. However, existing face alignment techniques tailored for visible-light (VIS) encounter a decline in accuracy when applied in NIR settings. This decline stems from the domain discrepancy between VIS and NIR facial domains and the absence of meticulously annotated NIR facial data.
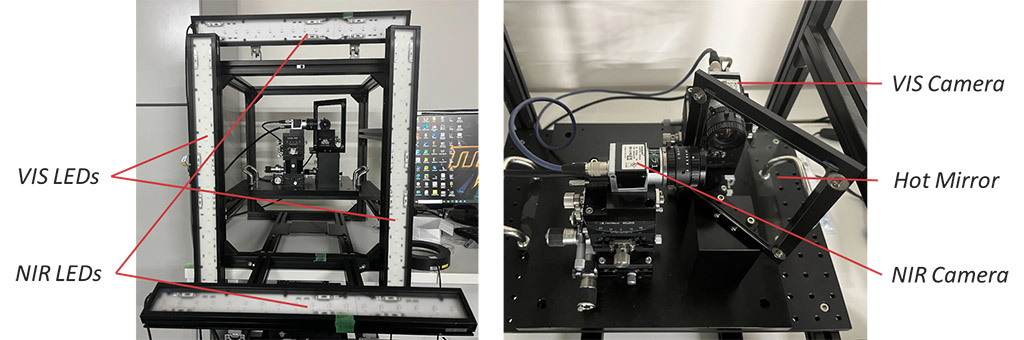
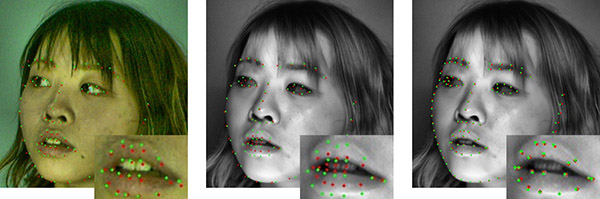
To address this issue, we introduce a system and strategy for gathering paired VIS-NIR facial images and meticulously annotating precise landmarks. Our system facilitates streamlined dataset preparation by utilizing automatic annotation transfer from VIS images to their corresponding NIR counterparts. Following our devised approach, we constructed an inaugural dataset comprising high-frame-rate paired VIS-NIR facial images with landmark annotations (1,200,000 images, 120 subjects, 98-point landmark annotations).

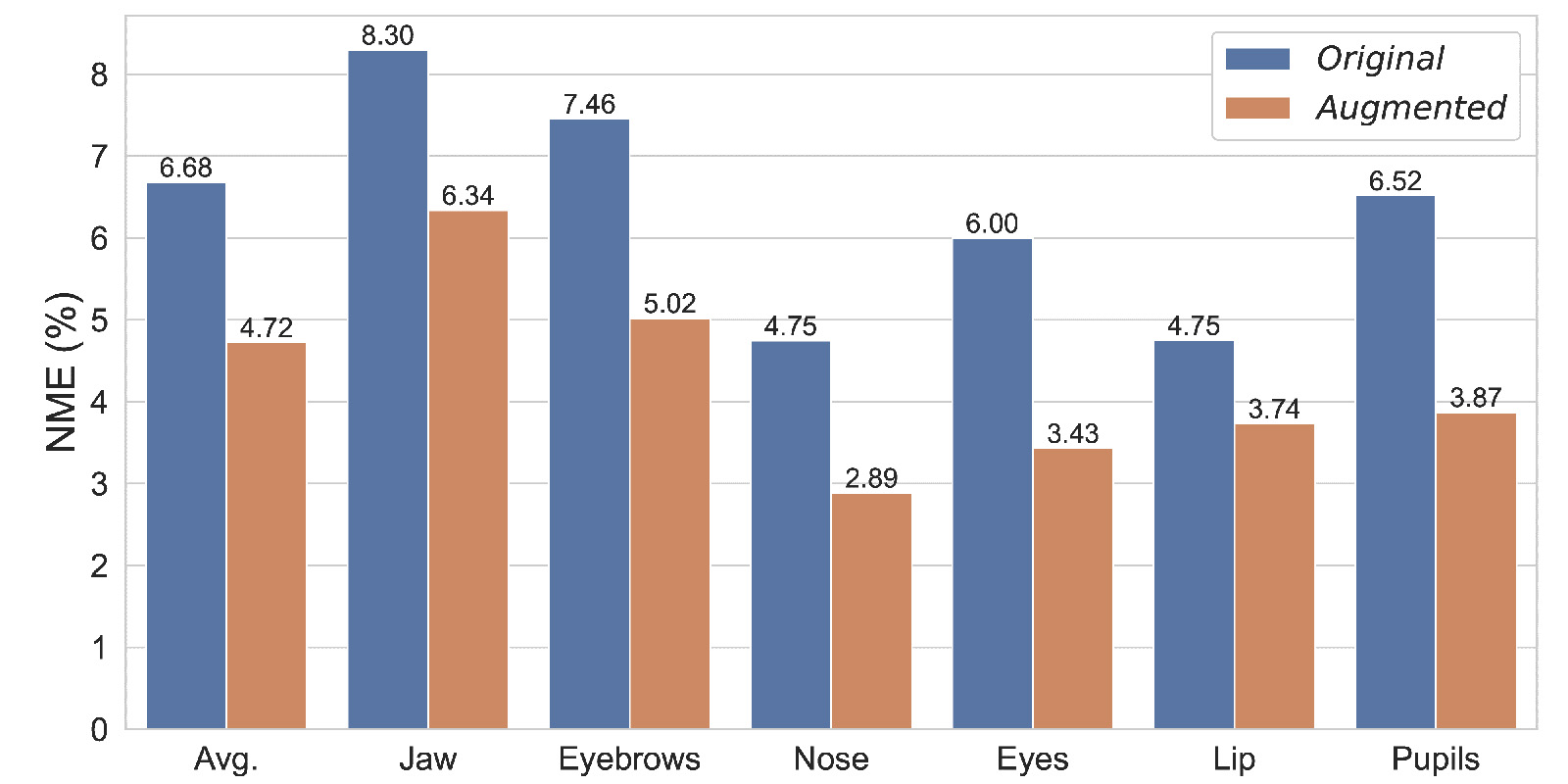
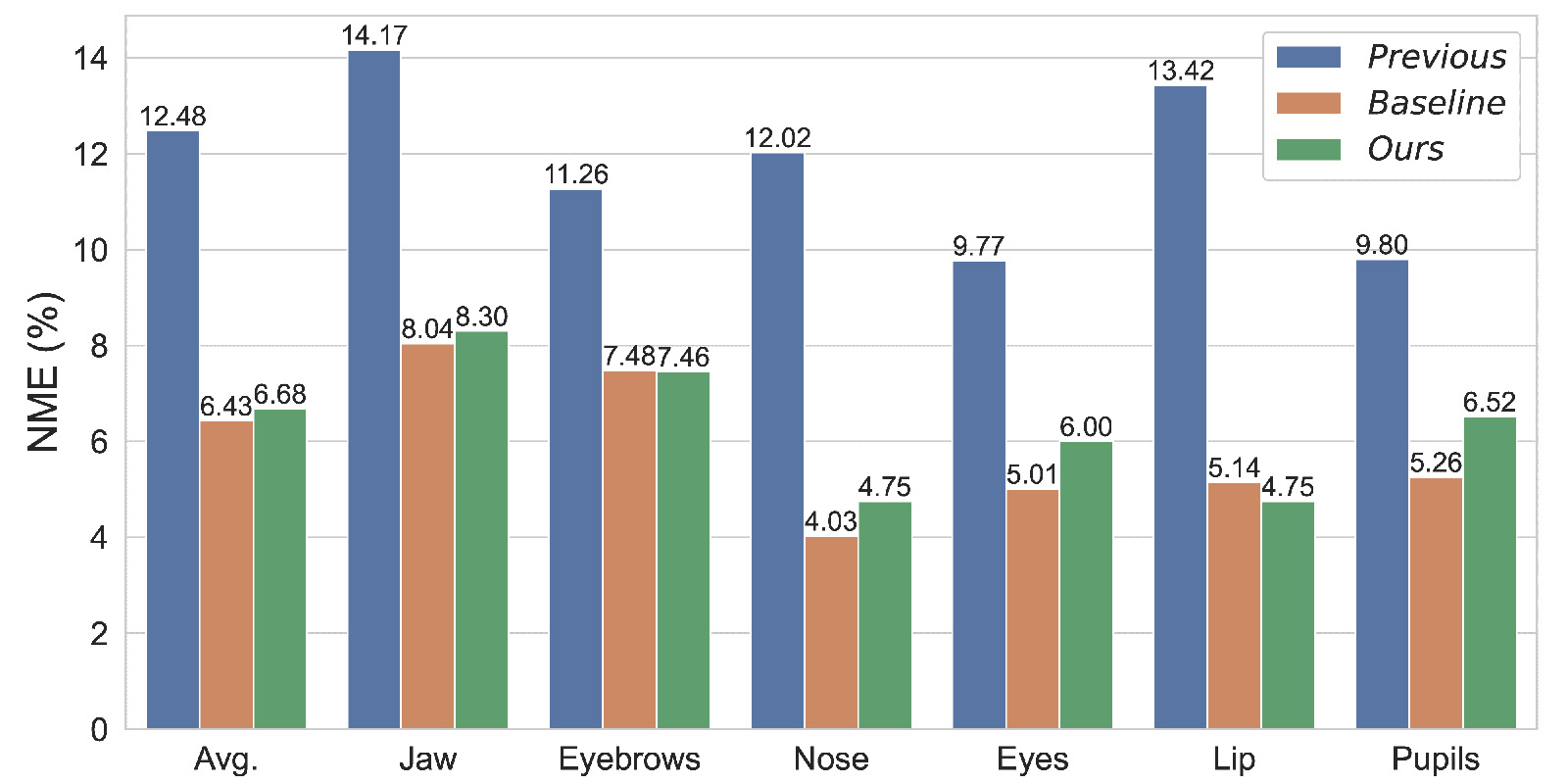
Additionally, to enhance the diversity of facial data, we augment our dataset through VIS-NIR image-to-image (img2img) translation using publicly available facial landmark datasets. Through the retraining of face alignment models and subsequent evaluations, our findings demonstrate a noteworthy enhancement in the accuracy of face alignment under NIR conditions using our dataset. Furthermore, the augmented dataset exhibits refined accuracy, particularly notable in the case of different individuals' facial features.
References
- Langning Miao, Ryo Kakimoto, Kaoru Ohishi and Yoshihiro Watanabe: Improving Real-Time Near-Infrared Face Alignment With a Paired VIS-NIR Dataset and Data Augmentation Through Image-to-Image Translation, 2024 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 2368-2374, doi: 10.1109/ICIP51287.2024.10648056, 2024.