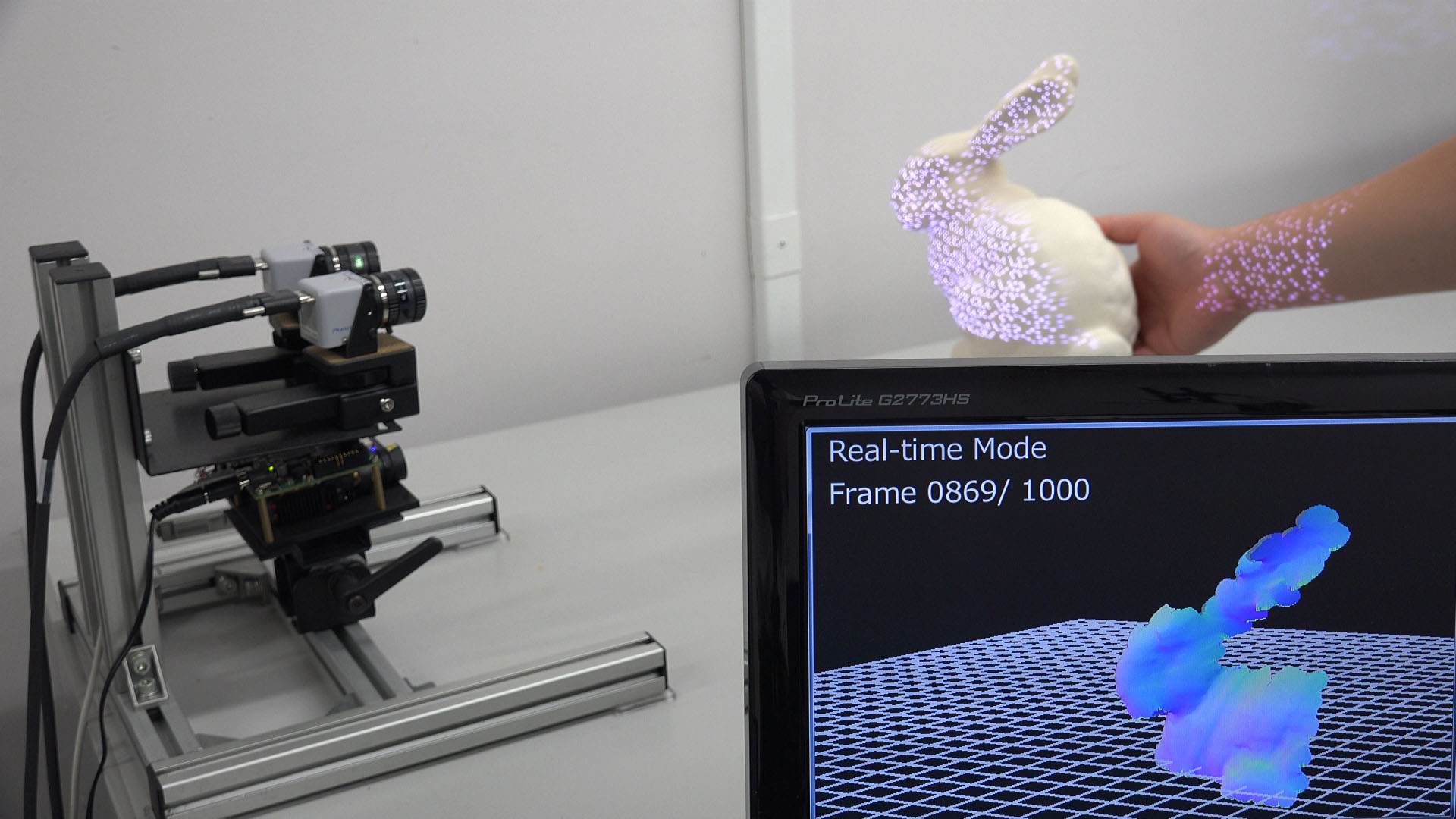
High-speed vision technology in which not just image capturing and recording but also image processing are executed simultaneously at high frame rates, exceeding video rates (30 Hz), has recently been considered an important technology for various applications, such as robotics, vehicle systems, automatic inspection, man-machine interfaces, sports science, and so on. However, the image processing performed in conventional high-speed vision systems is mainly based on two-dimensional pattern recognition. In order to extend the possibilities of this technology, here we focus on real-time three-dimensional sensing at the speeds achievable by high-speed vision systems. Although a related approach for high-speed 3D sensing can achieve a frame rate of over 200 fps, there are disadvantages, including the need for multiple captured frames during sensing, a limited measurement range and low resolution.
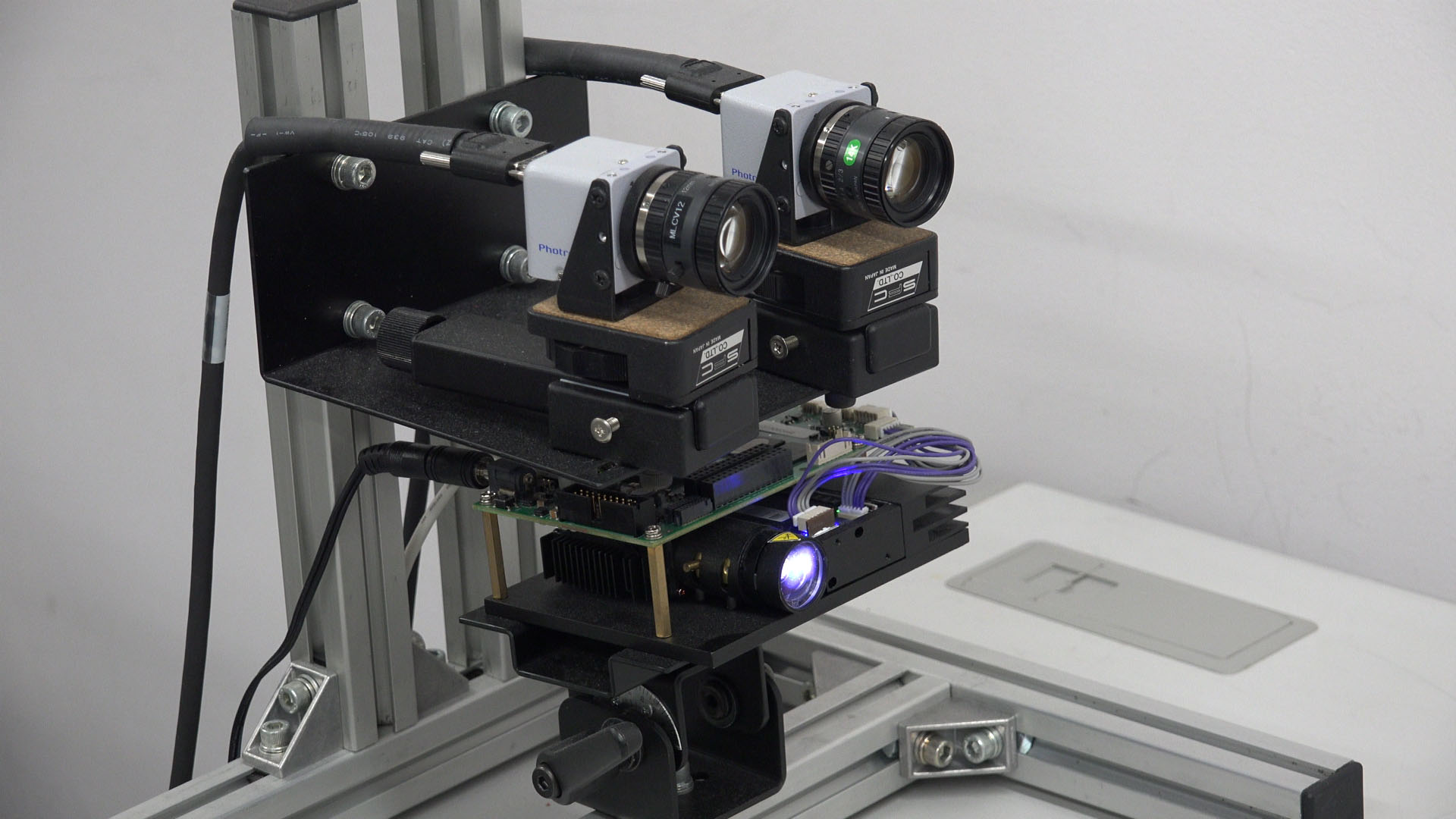
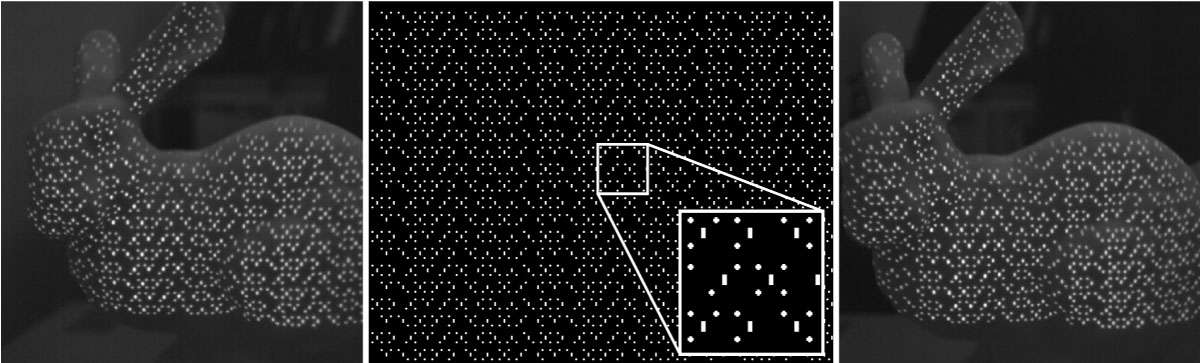
Our proposed real-time 3D sensing system consists of a projector and two cameras. By projecting a well-designed segmented pattern and using threeviewpoint epipolar constraints, the proposed system can obtain 3D points at high speed. In our method, the pattern is designed by using primitives. Each primitive consists of a bar and one or more dots. Incorporating the three-view geometry constraints eliminates the need for a given point in the pattern to have a unique feature in a local area compared with the other points when identifying corresponding points in different views. In this way, our method achieves high-speed and fine 3D point cloud acquisition with low latency based on hierarchical processing which is enabled by the segmented pattern and the three-view geometric properties. The developed system robustly obtained a 3D shape at 1000 fps in real time.


References
- Satoshi Tabata, Shohei Noguchi, Yoshihiro Watanabe, and Masatoshi Ishikawa: High-speed 3D Sensing with Three-view Geometry using a Segmented Pattern, 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) (Hamburg, 2015.9.30)/Proceedings, pp.3900-3907 (2015)